电磁检测是无损检测中的一种,用于查找物体中的缺陷。每种测试都有不同的应用和方法。所有测试都使用电场或磁场,有些测试同时使用电场或磁场。根据所使用的测试类型,电流或磁场的变化,当它通过或围绕被测试的物体发生电磁转化时,则信号指向可能存在的缺陷或缺陷。
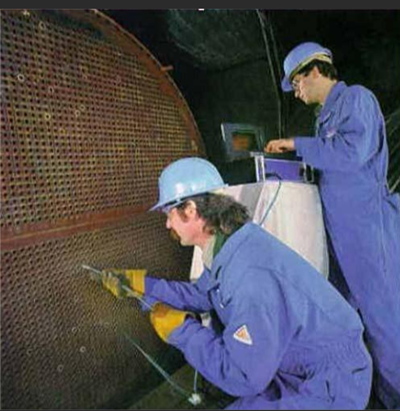
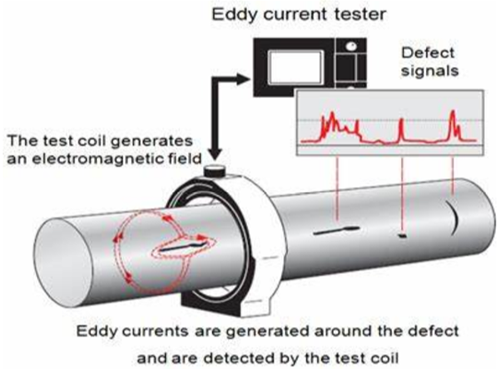
涡流检测技术是利用电磁感应原理,通过测定被检工件内感生涡流的变化来无损评定导电材料及其工件的某些性能,或发现缺陷的无损检测。
与涡流伴生的感应磁场与原磁场叠加,使得检测线圈的复阻抗发生变化。导体内感生涡流的幅值、相位、流动形式及其伴生磁场受导体的物理特性影响,因此通过监测检测线圈的阻抗变化即可非破坏地评价导体的物理和工艺性能,此即涡流检测的基本原理。
常规涡流检测是一种表面或近表面的无损检测方法。由于涡流因电磁感应而生,因此进行涡流检测时,检测线圈不必与被检材料或工件紧密接触,不需用耦合剂,检测过程不影响被检材料或工件的性能。
与其它无损检测方法比较,涡流检测的主要特点有:
对导电材料表面和近表面缺陷的检测灵敏度较高;应用范围广,对影响感生涡流特性的各种物理和工艺因素均能实施监测;不需用耦合剂,易于实现管、棒、线材的高速、高效、自动化检测;在一定条件下,能反映有关裂纹深度的信息;可在高温、薄壁管、细线、零件内孔表面等其它检测方法不适用的场合实施监测。涡流检测的缺点是检测效率相对较低;另外,仅依靠涡流检测通常也难以区分缺陷的种类和形状。




An electromagnetic test is a class of non-destructive testing used to find defects in an object. Each type of test has a different application and methodology. All tests use electricity or magnetic fields, with some using both. Depending on the specific type of testing used, the amount of electrical current that is reflected, refracted or otherwise conducted through the piece is measured. Changes in the current or magnetic field, as it moves through or around an object being tested, point to possible flaws or defects.
In the past, the term “electromagnetic test” typically referred to eddy-current testing. Eddy-current testing finds defects close to the surface of metal objects. Improvements in testing capabilities, however, have resulted in an ever-expanding number of electromagnetic test options. Other tests such as remote field testing, magnetic flux leakage testing, wire-rope testing and magnetic particle inspection allow users to test for defects in a variety materials, shapes and locations. Using electricity and magnetic fields, each type of electromagnetic test produces a response that points to cracks, heat damage, corrosion or other flaws in a broad range of materials and environments.
Aside from detecting defects, the use of electricity in magnetic fields can also help determine the other unseen properties of metal, earth and soft tissue. Results indicate material thickness, electrical conductivity, the presence of foreign objects and other information. The purpose of any electromagnetic test is to provide the ability to gather information before embarking on expensive or unnecessary digging, dissembling or surgery or to ensure the safety of a manufactured component.
Examples of the many uses of various types of electromagnetic testing can be found in commercial construction and the medical field. For example, pulsed eddy-current testing is used on pipes to determine metal loss without the need to expose the actual pipe. This type of electromagnetic testing can be done from a considerable distance when direct access to the pipe in question is not practical.

 鲁公网安备 37020602000203号
鲁公网安备 37020602000203号