1. X射线产生是由射线机内部通过电压击穿而产生的,其射线强度取决于射线机的电压。
2. r射线是由放射源衰变而产生的,下面是常见的放射源的半衰期
1)Co-60半衰期5.3年
2)Ir-192半衰期72天

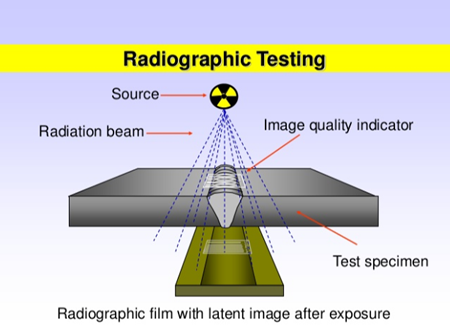

Radiography testing (RT) is one of the most widely used non destructive test (NDT) method. With the help of this method we can detect hidden flaws or discontinuities present in welds such as cracks, porosity & blow holes, slag, flux or oxide inclusions, lack of fusion, incomplete penetration, Mismatch and tungsten inclusion etc.
Short wavelength electromagnetic radiations such as X-rays or Gamma rays (γ) are used for Radiography testing. Both X-rays and Gamma rays have very high intensity and hence they are able to penetrate material of any thickness. This high penetrating power is used during radiography testing.
The material (being inspected) and the sensitive film are kept under exposure of radiation (either X-rays or Gamma rays) for a certain period of time then the film is developed. Once the film is developed, it is called as radiograph.
The density of the film or the amount of darkness on the film will vary depending upon the amount of radiation reaching the film. The darker area on a radiograph indicates more exposure (higher radiation intensity) as compared to the lighter areas which receives less exposure. This variation in the image darkness reveals the presence of flaws or discontinuity inside the film. This variation in the darkness may also be used to determine the thickness or composition of the test material.
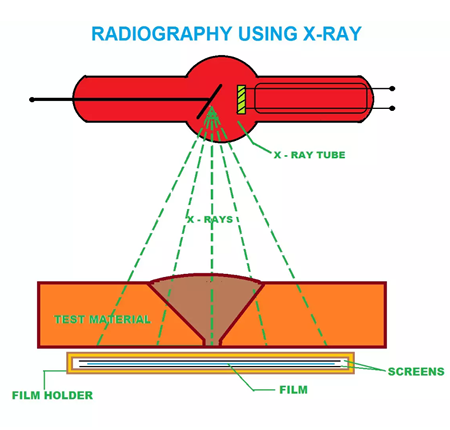
Radiography by using X-rays: X-rays are produced by an X-ray tube, which is an evacuated tube (usually made of glass) and it contains an electrically heated filament and a tungsten anode. The electrically heated filament releases electrons which are made to hit on the tungsten anode. Due to the collision of high velocity electrons with the tungsten anode, X-rays are emitted.
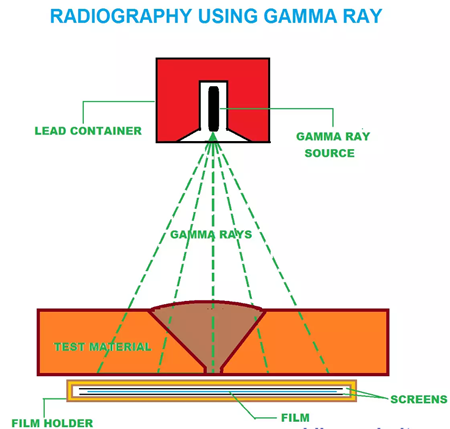
Radiography by using Gamma-rays: Gamma rays are produced by radioactive isotopes. Nucleus of a radioactive isotope remains unstable. Commonly used isotopes for industrial radiography are:
- Cobalt 60 (Co 60): Half-life of 5.3 years
- Iridium 192 (Ir192): Half-life of 72 days
Viewing Radiographs:
Radiographs (developed film exposed to x-ray or gamma radiation) are generally viewed on a light-box. However, it is becoming increasingly common to digitize radiographs and view them on a high resolution monitor.

 鲁公网安备 37020602000203号
鲁公网安备 37020602000203号